Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Sato, Takumi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(3), p.97 - 107, 2023/08
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has chosen nitride fuel as the first candidate for the transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MA) using accelerator-driven systems (ADS). The pyrochemical method has been considered for reprocessing spent MA nitride fuels, because their decay heat should be very large for aqueous reprocessing. This study was conducted to investigate the effect of decay heat on the pyrochemical reprocessing of MA nitride fuels. On the basis of the estimated decay heats and the temperature limits of the materials that are to be handled in pyrochemical reprocessing, quantities adequate for handling in argon gas atmosphere were evaluated. From these considerations, we proposed that an electrorefiner with a diameter of 26 cm comprising 12 cadmium (Cd) cathodes with a diameter of 4 cm is suitable. On the basis of the size of the electrorefiner, the number necessary to reprocess spent MA fuels from 1 ADS in 200 days was evaluated to be 25. Furthermore, the amount of Cd-actinides (An) alloy to produce An nitrides by the nitridation-distillation combined reaction process was proposed to be about one-quarter that of Cd-An cathode material. The evaluated sizes and required numbers of equipment support the feasibility of pyrochemical reprocessing for MA nitride fuels.
Nuclear Science and Engineering Center; Fuel Cycle Design Office; Plutonium Fuel Development Center; Nuclear Plant Innovation Promotion Office; Fast Reactor Cycle System Research and Development Center; J-PARC Center
JAEA-Review 2022-052, 342 Pages, 2023/02
This report summarizes the current status and future plans of research and development (R&D) on partitioning and transmutation technology in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, focusing on the results during the 3rd Medium- to Long-term Plan period (FY 2015-2021). Regarding the partitioning technology, R&D of the solvent extraction method and the extraction chromatography method are described, and regarding the minor actinide containing fuel technology, R&D of the oxide fuel production using the simplified pellet method, the nitride fuel production using the external gelation method, and pyrochemical reprocessing of the nitride fuel were summarized. Regarding transmutation technology, R&D of technology using fast reactors and accelerator drive systems were summarized. Finally, the new facilities necessary for the future R&D were mentioned.
 (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd using cadmium chloride
using cadmium chlorideHayashi, Hirokazu; Shibata, Hiroki; Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(2), p.503 - 510, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)The formation of MPd (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu -type GdPd
-type GdPd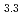 (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) and NpPd
0.0001 nm) and NpPd (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi
0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi -type NpPd
-type NpPd . Chlorination of the MPd
. Chlorination of the MPd (M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl
(M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl formation.
formation.
Tateno, Haruka; Sato, Takumi; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Hayashi, Hirokazu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(3), p.224 - 235, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:55.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fuel cycle technology for the transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MAs) using an accelerator-driven system has been developed using the double-strata fuel cycle concept. A mononitride solid solution of MAs and Pu diluted with ZrN is a prime fuel candidate for the accelerator-driven transmutation of MAs. Pyro-reprocessing is suitable for recycling the residual MAs in irradiated nitride fuel with high radiation doses and decay heat. Spent nitride fuel is anodically dissolved, and the actinides are recovered simultaneously into a liquid cadmium cathode via molten salt electrorefining. The process should be designed to achieve the target recovery yield of MAs and the acceptable impurity level of rare earths in the recovered material. We evaluated the material balance during the pyro-reprocessing of spent nitride fuel to gain important insight on the design process. We examined the effects of changing processing conditions on material flow and quantity of waste.
Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sasa, Toshinobu; Maekawa, Fujio; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Kurata, Masaki; Morita, Yasuji; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.657 - 663, 2015/09
To continue the utilization of the nuclear fission energy, the management of the high-level radioactive waste is one of the most important issues to be solved. Partitioning and Transmutation technology of HLW is expected to be effective to mitigate the burden of the HLW disposal by reducing the radiological toxicity and heat generation. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting the research and development on accelerator-driven subcritical system (ADS) as a dedicated system for the transmutation of long-lived radioactive nuclides. This paper overviews the recent progress and future R&D plan of the study on the ADS and related fuel cycle technology in JAEA.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Takano, Masahide; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Kurata, Masaki
NEA/NSC/R(2015)2 (Internet), p.360 - 367, 2015/06
Uranium-free nitride fuel was chosen as the first candidate for transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MA) using accelerator-driven system (ADS) under the double strata fuel cycle concept by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The advantages of nitride fuel are good thermal properties and large mutual solubility among actinide elements. A pyrochemical process is proposed as the first candidate for the reprocessing of the spent nitride fuel, because this technique has some advantages over aqueous process, such as the resistance to radiation damage, which is an important issue for the fuels containing large amounts of highly radioactive MA. This paper overviews the recent progress and future R&D plan of the study on the nitride fuel cycle technology in JAEA.
Ogawa, Toru; Minato, Kazuo; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nishihara, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 360(1), p.12 - 15, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:70.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The actinide management has become a key issue in nuclear energy due to increasing proliferation concern and long-term environmental perception. The better way of waste management will be made by system symbiosis: a combination of light-water reactor and fast reactor and/or accelerator-driven transmutation system should be sought. The new recycling technology should be able to achieve good economy with smaller plants, which can process fuels from different types of reactors on a common technical basis. Pyroprocess with the use of molten salts is regarded as the strong candidate for such recycling technology. In JAEA, the first laboratory for the high temperature chemistry of transuranium elements, mainly Am and Cm, has been established. The fundamental data on the molten-salt chemistry of transuranium oxides and nitrides will be combined with the computer code for predicting the molten-salts electrolytic processes.
Shirai, Osamu*; Yamana, Hajimu*; Arai, Yasuo
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1267 - 1273, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:84.47(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Minato, Kazuo; Akabori, Mitsuo; Tsuboi, Takashi; Kurobane, Shiro; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Takano, Masahide; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Misumi, Masahiro*; Sakamoto, Takuya*; Kato, Isao*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2005-059, 61 Pages, 2005/09
An experimental facility called the Module for TRU High Temperature Chemistry (TRU-HITEC) was installed in the Back-end Cycle Key Elements Research Facility (BECKY) of the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility (NUCEF) for the basic studies of the behavior of the transuranium elements (TRU) in pyrochemical reprocessing and oxide fuels. TRU-HITEC consists of three alpha/gamma cells shielded by steel and polyethylene and a glove box shielded by leaded acrylic resin, where experimental apparatuses have been equipped and a high purity argon gas atmosphere is maintained. In the facility 10 g of  Am as well as the other TRU of Np, Pu and Cm can be handled. This report summarizes the outline, structure, performance and interior apparatuses of the facility, and is the result of the joint research between the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and three electric power companies of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Tohoku Electric Power Co. and the Japan Atomic Power Co.
Am as well as the other TRU of Np, Pu and Cm can be handled. This report summarizes the outline, structure, performance and interior apparatuses of the facility, and is the result of the joint research between the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and three electric power companies of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Tohoku Electric Power Co. and the Japan Atomic Power Co.
 systems
systemsOkamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Suzuki, Shinichi; Minato, Kazuo; Tanida, Hajime*
Zeitschrift f r Naturforschung, A, 59a(11), p.819 - 824, 2004/11
r Naturforschung, A, 59a(11), p.819 - 824, 2004/11
The local structure of molten CdCl and CdCl
and CdCl -KCl mixture was investigated by high-temperature XAFS technique. The nearest Cd-Cl distance decreases by melting. Similarly, the coordination number decreases from 6 to 4. It suggests that there is (CdCl
-KCl mixture was investigated by high-temperature XAFS technique. The nearest Cd-Cl distance decreases by melting. Similarly, the coordination number decreases from 6 to 4. It suggests that there is (CdCl )
) tetrahedral complex ion in the melt. It is concluded that the local structure is kept also in the mixture melt, since the same XAFS result as the pure melt was obtained.
tetrahedral complex ion in the melt. It is concluded that the local structure is kept also in the mixture melt, since the same XAFS result as the pure melt was obtained.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Minato, Kazuo
JAERI-Conf 2004-008, 228 Pages, 2004/04
Applications of molten salts technology to separation and synthesis of materials have a potential to give us a civilized life, for example aluminium refinement. Recently, much attention is given to the pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels in the molten salt research field. On the other hand, computer simulation technique is expected to play an important role for supporting experimental works and predicting unknown physical properties in the molten salts application studies. Research group for Actinides Science, Department of Materials Science, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI), together with Reprocessing and Recycle Technology Division, Atomic Energy Society of Japan, organized the 3rd Workshop on Molten Salts Technology and Computer Simulation at Tokai Research Establishment, JAERI on December 16, 2003. Many molten salts researchers in Japan participated in the workshop and many useful presentations and discussions were performed.
Watanabe, Takeshi*; Tsushima, Satoru*; Yamamoto, Ichiro*; Tomioka, Osamu; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Mikio; Wada, Ryutaro*; Nagase, Yoshiyuki*; Fukuzato, Ryuichi*
Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Supercritical Fluid Technology for Energy and Environment Applications (Super Green 2003), p.363 - 366, 2004/00
Recovery of salts by supercritical fluid leaching (SFL) method using carbon dioxide was experimentally studied. It was confirmed that LiCl was recovered with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide and methanol, and KCl and SrCl were recovered with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide, methanol and crown ether. The influence of crown ether for KCl and SrCl
were recovered with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide, methanol and crown ether. The influence of crown ether for KCl and SrCl extraction were found to increase in the order of 15-crown-5 (15C5)
extraction were found to increase in the order of 15-crown-5 (15C5)  18-crown-6 (18C6)
18-crown-6 (18C6)  dicychlohexyl-18-crown-6 (DC18C6). It is expected that other salts can be recovered selectively with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide, methanol and suitable crown ether.
dicychlohexyl-18-crown-6 (DC18C6). It is expected that other salts can be recovered selectively with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide, methanol and suitable crown ether.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Minato, Kazuo
JAERI-Conf 2003-005, 186 Pages, 2003/06
Applications of molten salts technology to separation and synthesis of materials have been widely studied. Especially, much attention is given to the pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels. Computer simulation technique is expected to play an important role for supporting experimental works and predicting unknown physical properties in the molten salts application studies. Research group for Actinides Science, Department of Materials Science, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), together with Reprocessing and Recycle Technology Division, Atomic Energy Society of Japan, organized the 2nd Workshop on Molten Salts Technology and Computer Simulation at Tokai Research Establishment, JAERI on December 3, 2002. Many molten salts researchers in Japan participated in the workshop and many useful presentations and discussions were performed.
Shirai, Osamu*; Yamana, Hajimu*; Iwai, Takashi; Arai, Yasuo
Proceedings of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Technologies Closing the Fuel Cycle (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2003/00
no abstracts in English
Arie, Kazuo*; Abe, Tomoyuki*; Arai, Yasuo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 44(8), p.593 - 599, 2002/08
no abstracts in English
Arai, Yasuo
Nenryo Saikuru Gijutsu; 21-Seiki No Nenryo Saikuru No Kochiku Ni Mukete, p.119 - 126, 2002/05
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinichi; Morita, Yasuji; Nishihara, Kenji
Proceedings of International Conference on Back-End of the Fuel Cycle: From Research to Solutions (GLOBAL 2001) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2001/09
Production of lower-level radioactive wastes, as well as the reduction in radioactivity of HLW, is an important performance indicator in assessing the viability of a partitioning-transmutation system. We have begun to identify the chemical compositions and to quantify the amounts of radioactive wastes that may be generated by JAERI's processes. Long-lived radionuclides such as  C and
C and  Ni and spallation products of Pb-Bi coolants such as
Ni and spallation products of Pb-Bi coolants such as  Po (10
Po (10 Bq/yr) are added to the existing inventory of these nuclides that are generated in the current fuel cycle. Spent salts of KCl-LiCl, which is not generated from the current fuel cycle, will be introduced as a waste.
Bq/yr) are added to the existing inventory of these nuclides that are generated in the current fuel cycle. Spent salts of KCl-LiCl, which is not generated from the current fuel cycle, will be introduced as a waste.
Arai, Yasuo
Saishin Kaku Nenryo Kogaku; Kodoka No Genjo To Tembo, p.451 - 457, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinichi; Morita, Yasuji; Nishihara, Kenji
Proceedings of International Conference on Back-End of the Fuel Cycle: From Research to Solutions (GLOBAL 2001) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinichi; Morita, Yasuji; Nishihara, Kenji
KURRI-KR-57, p.55 - 62, 2000/11
no abstracts in English